.jpg)

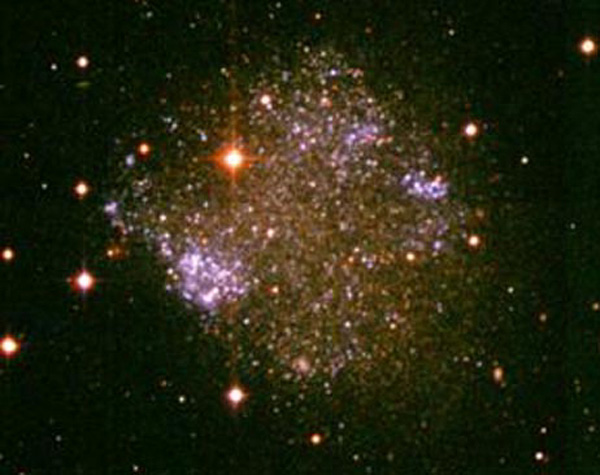
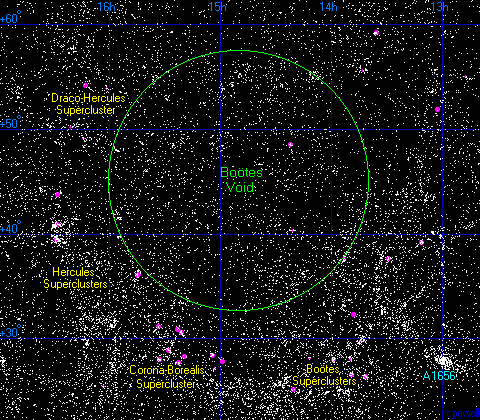
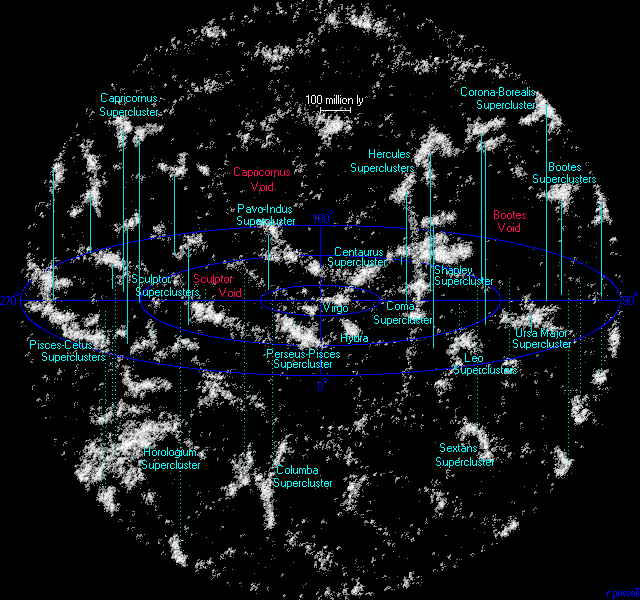
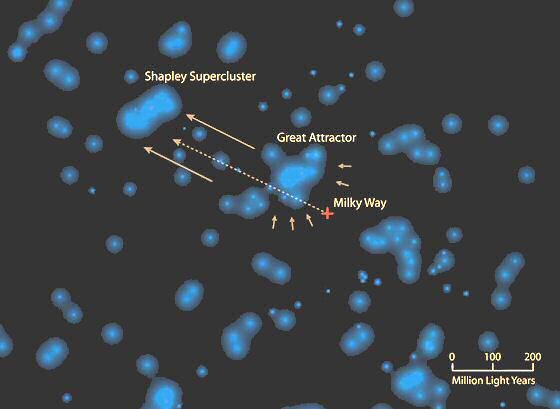
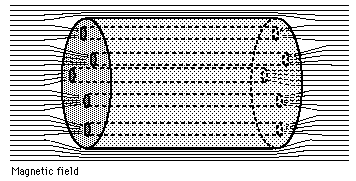
Hyperclusters are composed of local groups of superclusters, and would require over 100 billion years to form. This means that the vast VOIDS are not empty, but are turbulent magnetic fields between superclusters, that connect to hyperclusters by gigantic filaments, many larger then the sloan great wall filament, spanning over 1.37 billion light years across. The Universe must be filled with innumerable hyperclusters that form fractal filamentary structures. Stenflo in "Solar Magnetic Fields" 2008 identifies on the sun's surface, a widespread "fractal-like pattern of voids, that are teeming with turbulent magnetic fields." The Virgo Supercluster is about 110 million light years across, and contains about 100 galaxy groups and clusters. The larger southern Local supervoid near our local supercluster has 600 billion times the volume of our galaxy.
In "Inhomogeneities in the Universe" Francesco Sylos Labini wrote "the observed galaxy structures are not compatible with the standard LCDM (cold dark matter) model of galaxy formation." "Inhomogeneities pose a fundamental challenge to standard big-bang cosmology." Michael J Hudson wrote on Cosmic Smoothness, "This result is not entirely new, previous studies based on subsets of the data studied by Shaun Thomas showed the same effect." "If the inhomogeneity is confirmed, the implications for the big-bang standard model would be severe, including that for dark matter and dark energy." Hudson uses quotation marks, referring to the "cosmic web" as filaments, but states it is too soon to discard the standard model. Alfven proposed a plasma hierarchy of structures in the Universe, which includes the galactic corona, and the hottest densest known plasma medium pervading Galaxy Clusters. Most likely there are no laws or rules in the Universe to limit the size of plasma structures. Atoms, stars, galaxies, galaxy clusters, superclusters, hyperclusters...and ever larger and smaller plasma structures all simultaneously exist together having their own relative time. There is no smallest particle to be found, nor largest structure in the universe. In fact the universe is such that everyone cannot reach a common definable description of agreement. Space is never empty, because some smaller particles can always be found between the distances that larger objects are apart. Size is relative to comparisons of objects. Is true empty space without objects or particles absolute emptiness or nothing? Everything is not nothing, so why must there be something rather then nothing, and an "everything?"
 |
| Hyperclusters of galaxies |

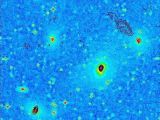
 The Universe is filled with vast Hyperclusters, that challenge the standard Big-bang cosmological model. Shaun Thomas of Univ. College London and colleagues have found aggregations of galaxies stretching for more than 3 billion light years. Anomalous signatures given by excess power over large scales imply a large anomaly, with a couple of percent variation in density from place to place, but a huge density contrast that is twice what theory predicts. Elliptical galaxies in a new MegaZ DR7 volume galaxy survey photometric catalogue, have the highest photometric redshifts. These most distant and oldest known galaxies are forming Hyperclusters !
The Universe is filled with vast Hyperclusters, that challenge the standard Big-bang cosmological model. Shaun Thomas of Univ. College London and colleagues have found aggregations of galaxies stretching for more than 3 billion light years. Anomalous signatures given by excess power over large scales imply a large anomaly, with a couple of percent variation in density from place to place, but a huge density contrast that is twice what theory predicts. Elliptical galaxies in a new MegaZ DR7 volume galaxy survey photometric catalogue, have the highest photometric redshifts. These most distant and oldest known galaxies are forming Hyperclusters !
12 billion light year scale view by BOSS