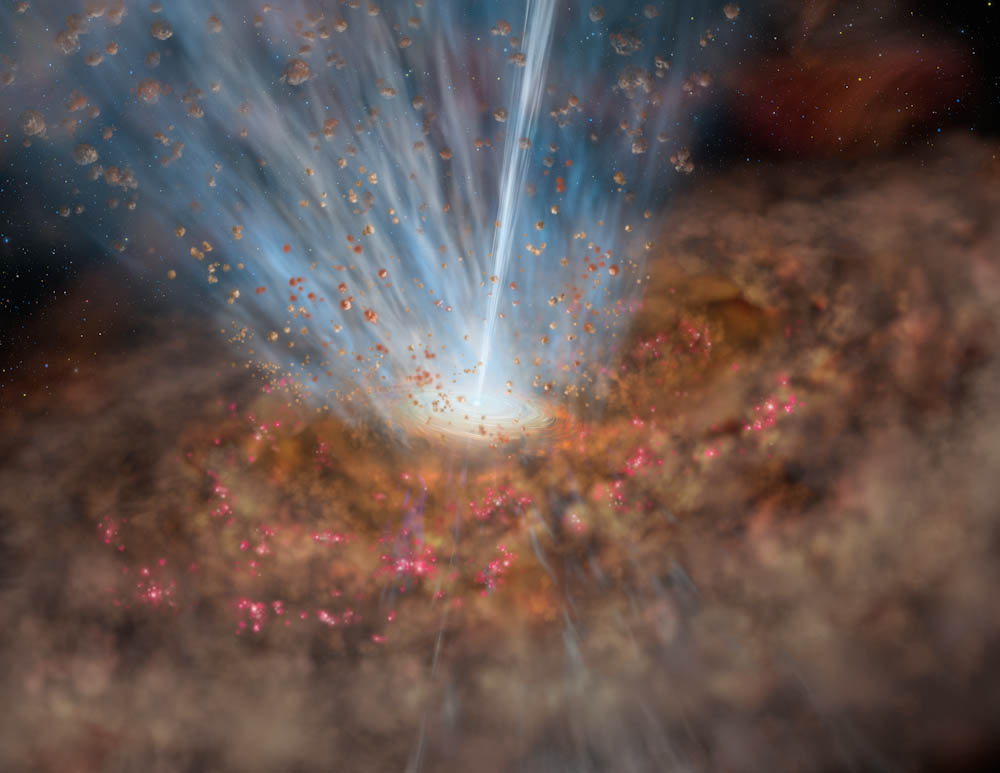
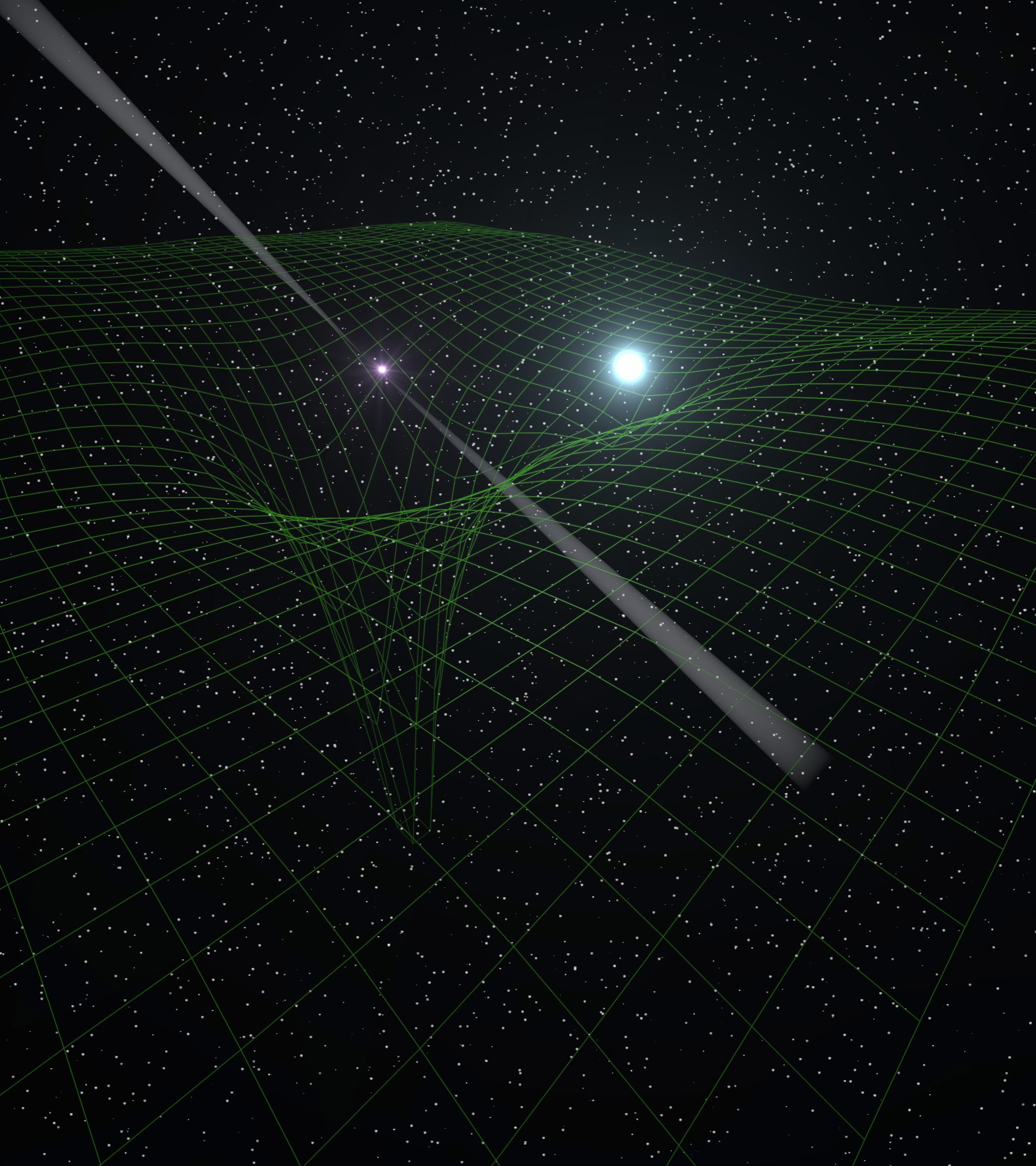
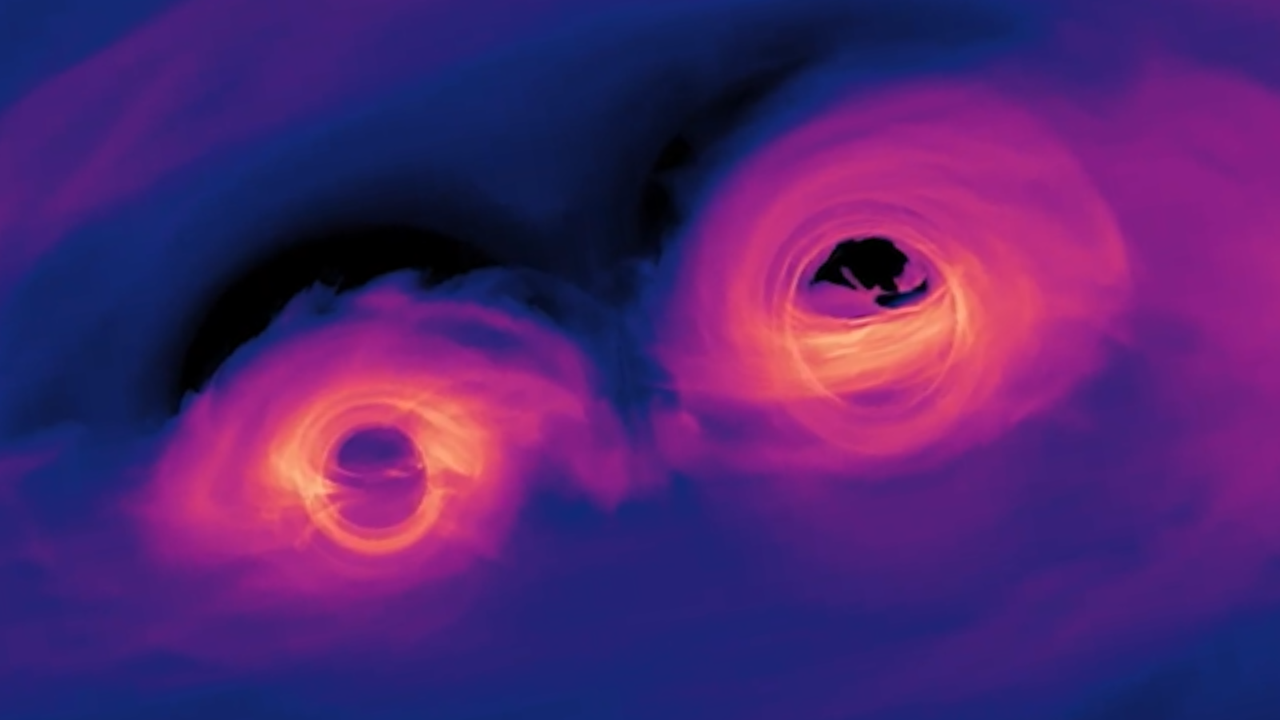
Kyle Stewart's computer simulation shows how Galaxies grow by feeding on cold gas swirling into the theoretically inferred singularity region at the galactic core center. Stars form by condensation inside cold filaments, especially near galaxy centers. Stewart writes that "Galaxies came to be from bits of matter that were connected together by filaments." Cold gas follows the filaments and flows into the galaxy center faster than previously believed, and dark matter also funnels faster than previously believed into the galaxy center along the filaments. It's just as if the cold magnetized plasma gaseous filaments actually produce their need for inventing and attaching a dark matter gravitational force. Cold filaments containing single atom thick liquid helium atoms have inherent magnetic levitation phenomena, that can fully refute and explain away the problematic dark matter mystery and gravitational singularity.
Cold Gas Filaments Swirl Into a Singularity to Feed Growing "Black Holes" finds Kyle Stewart.
Cold Fronts Shape the Formation of Galaxies - Plasma astrophysics is the realm for new cosmology.
"Sloshing Cold Fronts in Galaxy Groups like IC 1860 Shape New Formation Models"
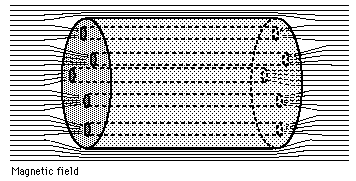
Video: Quantum Vortices in Superfluid Helium mathematically analogs relativity, mimicking gravitational black hole physics. Cosmic scale self-similar galactic filaments are in a vortex state, that compares to the physics of quantum vortices in superfluid helium. Magnetic levitation phenomena of superfluid helium is well demonstrated in labs. Cold filaments connect to spinning galaxy superfluid core regions shaping cosmic phenomena by magnetic fields, instead of by dark matter and black holes. Quantum vortices carry the angular momentum of the superfluid, and are theoretically similar to a superconductor's flux lines that carry the magnetic field created by electric current traveling through them. Electromagnetism shapes the Universe.
Spiraling Cold Gas Funnels Into Theoretically Unseen Black Holes. Helium-4 atoms behave as a single entire whole collective entity, when condensing into a superfluid. Filaments connect together the spiral arms of a galaxy with it's spinning black hole core region.
Kostas Skenderis links Negatively Curved Space-Time and Flat Space-Time, with the Gregory Laflamme instability. New Mathematical Model Links Negatively Curved Space-Time and Flat Space-Time
The Gregory Laflamme instability grows stronger by spin and rotation, breaking up a large superfluid helium comprised black hole into many smaller self-similar fractal droplets. It is a phase change resembling a stream of water breaking up into water droplets, or superfluid helium. Black holes were discovered to break apart into smaller ones, which remained unexplainable until recent discoveries are applied to cosmology.
Cold Gas Filaments Swirl Into a Singularity to Feed Growing "Black Holes" finds Kyle Stewart.
"Sloshing Cold Fronts in Galaxy Groups like IC 1860 Shape New Formation Models"
Spiraling Cold Gas Funnels Into Theoretically Unseen Black Holes. Helium-4 atoms behave as a single entire whole collective entity, when condensing into a superfluid. Filaments connect together the spiral arms of a galaxy with it's spinning black hole core region.
It's All "Hot Air" That Galaxies Form by Gravity!!
The previous standard gravity model of galaxy formation held that hot gas sank inwards into the centers of galaxies from all directions and got hotter. Cold-Mode theory shows gas is not being heated by gravitational contraction and collapse. New cosmological models require the existence of superfluid helium as constituents for the formation of stars and galactic black hole inferred centers. The phase change of liquid to superfluid helium just below 2.17 degrees Kelvin involves no latent heat, nor any specific volume change. No heat is released by the cold gaseous filament during the phase change of helium.Kostas Skenderis links Negatively Curved Space-Time and Flat Space-Time, with the Gregory Laflamme instability. New Mathematical Model Links Negatively Curved Space-Time and Flat Space-Time
The Gregory Laflamme instability grows stronger by spin and rotation, breaking up a large superfluid helium comprised black hole into many smaller self-similar fractal droplets. It is a phase change resembling a stream of water breaking up into water droplets, or superfluid helium. Black holes were discovered to break apart into smaller ones, which remained unexplainable until recent discoveries are applied to cosmology.